RISC-V ASM / Payloads Part 1
⊕ 2019-03-17
RISC-V is a relatively new architecture (2010) that has been getting some press and attention for various reasons, and has garnered some enterprise adopters such as NVIDIA and Western Digital. Recently, other organizations have begun creating physical silicon and virtualization support. It is no longer vaporware. It’s openness also allows for a unique ability to just go to the projects git repositories and find documentation.
A new instruction set architecture is always interesting, but provides a unique opportunity for me to attempt to learn about a topic without all the research being completely done for me.
It’s easy to feel like you are standing on the shoulders of giants in the security field and not gain the knowledge yourself by struggling. Which is why I decided that I would go down the path of writing RISC-V payloads and shellcode by hand without using any other resources than those provided by RISC-V and some prior light assembly knowledge with the goal of documenting my learning process step by step.
src
The code and documentation for this project is mirrored on my git repos:
The README in the root of the project gives a rough breakdown of how I
plan on structuring these walk-throughs and if you aren’t a reading along
with a blog post type I have embedded pretty detailed comments in the
assembly files themselves. Part 1 will only cover the very basics of the
ISA and get to the example asm1.s.
docs
During this project the following supporting or helpful documents were used:
- RISC-V User-Level ISA (2019-03-28 version)
- RISC-V Green Card
- Linux RISC-V Kernel
- Linux Architecture Specific syscall(2) Info
- Fedora RISC-V Images
setup
When I first tried to play with RISC-V it required using the git versions of glibc, gcc, qemu, the Linux kernel, etc. I had to build my own images to boot into qemu and cross my fingers that things would work as expected, flaky would be the polite version.
Luckily, distributions have even caught on and Debian, Fedora, and somewhat Alpine have varying degrees of support. For these I ended up using the pre-built images from fedora using the information here, this has a lot more realistic tooling and work pretty flawlessly.
More complete instructions are located in the git repositories listed above.
Once you have a basic image booted and accessible, ensure that a few
core tools are available: gcc, objdump, strace, and gdb.
basics
The very first steps I took were to read the RISC-V ISA specification from front-to-back. This helped clarify a couple of questions I had and also lead me to a couple of questions that could only be answered by reading the actual implementation code.
Distilled down RISC-V contains 3 officially supported word-widths (32, 64, and 128), 32 registers, and 7 official instruction extensions.
The registers are all referred to as x0-x31, but have a register
convention
defined in the following table:
| Name | Mnemonic | Use | Preserved |
|---|---|---|---|
| x0 | zero | Zero | Immutable |
| x1 | ra | Return address | No |
| x2 | sp | Stack pointer | Yes |
| x3 | gp | Global pointer | N/A |
| x4 | tp | Thread pointer | N/A |
| x5-x7 | t0-t2 | Temporary registers | No |
| x8-x9 | s0-s1 | Callee saved registers | Yes |
| x10-x17 | a0-a7 | Argument registers | No |
| x18-x27 | s2-s11 | Callee saved registers | Yes |
| x23-x31 | t3-t6 | Temporary registers | No |
instruction types
In RISC-V each instruction is designated one of 6 “types” which are the
format in which the arguments of the instruction are structured when
they are read by the CPU. The core set of these is referred to as
RV{32,64,128}I (for shortness sake this post will use the RV64
signature from now on) where the number is the word length, we will
refer to this as the core I instructions. The best way to see this is
to visualize it:

Looking at the above table we can see the types and the bit formatting.
I found this a bit confusing at first so to break it down let’s look at
ADD which is type R.
ADD in assembly is structured like ADD rd,rs1,rs2 or in mathematical
format rd = rs1 + rs2. Knowing this we know that ADD puts the hex
representation of the two source registers and the destination, those
are relatively clear. But what are funct7 and funct3? When the
opcode is set funct3 and funct7 select additional operation
arguments, so in this case ADD shares an opcode with 9 other
instructions. funct3 selects the opcodes 3-bit “sub-function” and
funct7 further modifies functionality. Using a terrible one liner that
we will talk about later we can view what ADD a0,a7,a6 looks like:
# ./util/trashfmt.py $(./util/trashdis.sh "ADD a0,a7,a6")
00000001 00001000 10000101 00110011

I really like the way the ISA manual shows this Chapter 25, with the
individual opcodes and functNs filled out.
extensions
In addition to the RV32I instructions there current 8 other extensions
officially supported by the RISC-V ISA that will depend on the hardware.
A listing of what some of those extensions are can be seen below:
- M - Integer multiplication and division
- A - Atomic instructions
- F - Single-precision floating point
- D - Double-precision floating point
- Q - Quad-precision floating point
- L - Decimal floating point
- C - Compressed instructions
- B - Bit manipulation
- J - Dynamically translated languages*
- T - Transactional memory*
- P - Packed-SIMD*
- V - Vector operations*
- N - User-level interrupts*
- Zicsr - Control and status register
- Zefencei - Instruction-fetch fence
NOTE: * denotes non-G extensions
Luckily the RISC-V team has decided to organize a sub-section of
these into what they consider to be a “general-purpose” ISA, which will
contain RV64IMAFD + Zicsr/Zefencei. As much as that has a nice ring to
it, that can be abbreviated to RV64G. In my experience with emulators
and the few pieces of hardware out there, most are currently RV64GCU
to include the compressed extension. Because of that I’m going to
also have a few examples with “compressed” enabled as it can drastically
help show how to shrink our payloads and in some cases remove the need
for executable stack in some situations.
The VM I am using from Fedora has the following CPU configuration from
/proc/cpuinfo:
processor : 0
hart : 3
isa : rv64imafdcu
mmu : sv48
... snip ...
The u is additionally not a real extension, but is an indicator that
the cpu is running in unprivileged mode.
linux & glibc
Now that we understand the instructions and their extensions we can move on to understand how current operating systems are interacting with RISC-V. For the sake of purely adoption numbers and nothing else I will be focusing on the glibc and Linux implementations of RISC-V.
The first steps to understand the interaction of libc and Linux work with RISC-V is to dive straight to the system dependent source and documentation:
Most of these definitions are for setting up the logic for system calls and any other specific ISA requirements for Linux. The main part we are going to focus on for now is the system calls using the calling convention in the first table in the post.
system calls
When dealing with embedded payloads and shellcode generically it’s always important to keep a in mind that you cannot always make guarantees about the system you are running on and one of the more consistent ways to ensure that your payloads are going to work on Linux is to rely on kernel builtin system calls.
The glibc code gleans a lot about how Linux, glibc, and RISC-V interact,
and the system specific documentation on the syscall(2) man page
essentially confirms and clarifies the glibc code.
The important bits for now are that RISC-V expects system calls to use
argument a0-a6 and then set the syscall value in a7.
Documentation for the syscall(2) can be found in
source
or on the local VM in /usr/include/asm-generic/unistd.h. These values
are the integers that we are loading into a7 to invoke the system
calls. Once the syscall is loaded we do something similar to syscall
/int 80 in x86_64, use the environment call ECALL instruction.
Once the system call is handled any return values are loaded into a0,
which we will use to help shrink some of our payloads later on.
Many syscall’s are wrapped by libc’s and you should make sure to use the kernel versions of the calls and not what is expected from the libc.
pseudoinstructions
In the instruction land it is important to note one additional thing, the assembler understands a set of pseudoinstructions. The pseudoinstructions are linker understood instructions that are aliases for common functions, the table of these can be seen in Table 26.2 with a translation of what the instructions are translated to.
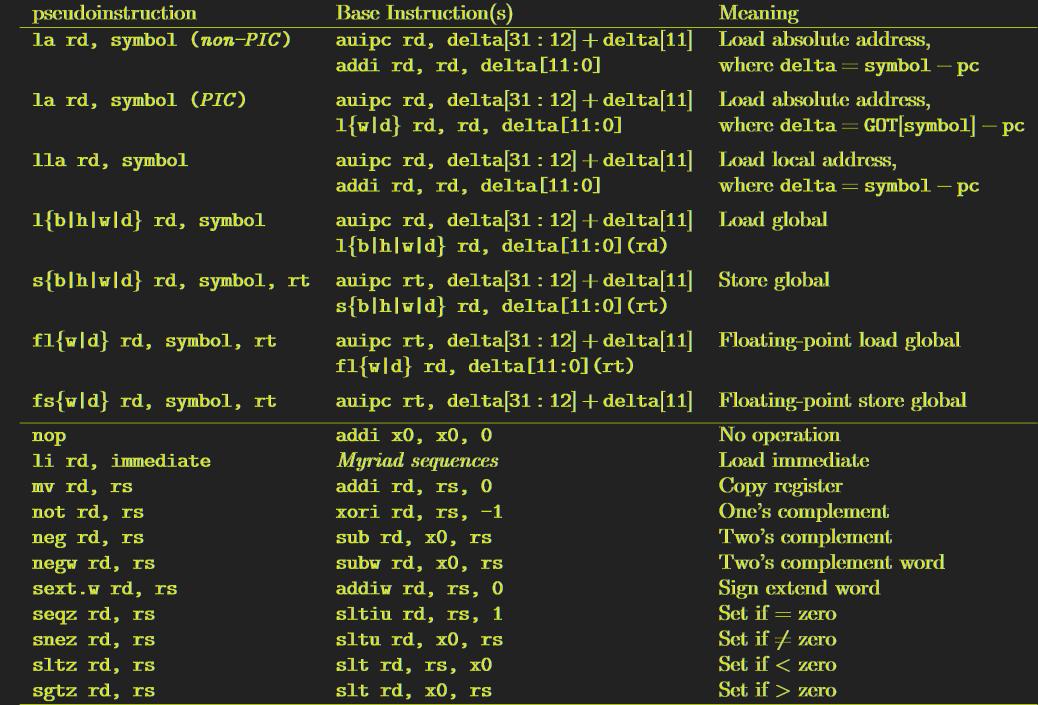
This tripped me up for an embarrassingly long time as certain
instructions may generate their translated into different instructions
in different contexts. The best example is the li pseudo-instruction
that may generate different code depending on data is being loaded. The
confusing-ness is even more confusing based on the ISA specification
specifically stating that “This chapter is a placeholder for an assembly
programmer’s manual” which is not particularly helpful.
We will go into more depth once we actually need to make the instructions predictable for our payloads.
asm1.s: syscall
Enough with the theory! Now that we have all the pieces that we need to really understand how to write assembly in RISC-V, lets put that into practice.
Our first example will simply exit the program with a value of 7.
To set this up we need to load our exit value (7) into the first
argument for the system call. As stated before many syscall’s are
wrapped by libc and you should make sure to use the kernel versions of
the syscalls from unistd.h. In my case this was the value of
__NR_exit, which was defined as 93.
The first part of this clears the a0 register using RV64G standard
instructions. The second uses the li pseudoinstruction to load the
systemcall number. These effectively do the same thing, but demonstrate
the usage of pseudo-instructions when we decompile it:
.section .text
.globl _start
_start:
xor a0,a0,a0 # Zero out the first argument (a0)
addi a0,a0,0x7 # Add 7 to a0. addi dest,src,immediate
li a7, 93 # 93 is the __NR_exit syscall
ecall # trigger system call
That’s it. Generate this by running make asm or compiling and linking
it yourself with gcc. I compiled these with the explicit
-march=rv64g since the VM is running RV64GCU, as explained earlier.
We can verify that the compiler did what we wanted (or what it did with
the li pseudo-instruction) by doing an objdump -D bin/asm1.
$ objdump -D ./bin/asm1
bin/asm1: file format elf64-littleriscv
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000010078 <_start>:
10078: 00a54533 xor a0,a0,a0
1007c: 00750513 addi a0,a0,7
10080: 05d00893 li a7,93
10084: 00000073 ecall
A simple run and check for the return value confirms this, and an
strace shows it even better:
$ ./bin/asm1
$ printf "%i\\n" "$?"
7
$ strace ./bin/asm1
execve("./bin.asm1", ["./bin/asm1"], 0x3fffddd4a0 /* 33 vars*/) = 0
exit(7) = ?
+++ exited with 7 +++
Now we have our very first example done! This is extremely rudimentary but helped me understand some of the terminology that I was struggling to infer.
part 2
Part 2 will contain more complex examples, exploring endianness, the
stack, a look at the li pseudoinstruction, debugging, and some RISC-V
immediate usage.